
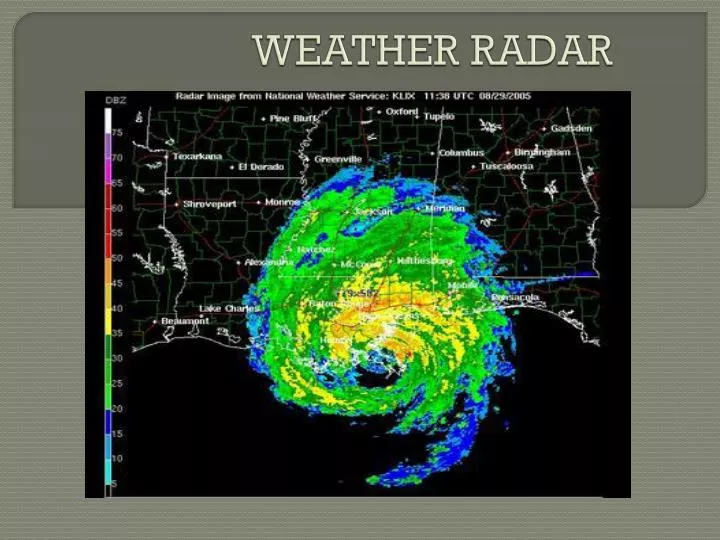
Heavy rainfall is possible over Kerala and Mahe.Very heavy showers are forecast over Rayalaseema.Extremely heavy rainfall is possible in isolated places of Coastal Andhra Pradesh, Yanam, Tamil Nadu, Puducherry and Karaikal.Fairly widespread rainfall and thunderstorms are expected over Coastal Andhra Pradesh, Yanam, South Interior Karnataka, Kerala, Mahe, and Lakshadweep.Widespread rains and thunderstorms are likely over Andaman & Nicobar Islands, Rayalaseema, Tamil Nadu, Puducherry and Karaikal.Dry weather is expected in other areas.Dense fog is possible over inland areas of North and Central India early in the morning.Isolated rains are likely over Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Meghalaya, Sub-Himalayan West Bengal, Sikkim and Coastal Karnataka, with a chance of lightning.Scattered showers with isolated thunderstorms are likely over Andaman & Nicobar Islands, South Interior Karnataka, Kerala, Mahe, and Lakshadweep, with heavy rainfall possible over Kerala and Mahe.Very heavy rainfall is likely over Rayalaseema.Extremely heavy rainfall is possible in isolated places of north Coastal Andhra Pradesh, Yanam, Tamil Nadu, Puducherry and Karaikal.Fairly widespread showers and thunderstorms are likely over Andhra Pradesh.Widespread rains and thunderstorms are likely over Tamil Nadu, Puducherry and Karaikal.This area is commonly referred to as the radar’s “Cone of Silence”.Here's the weather outlook for India: Friday (November 11) Therefore, close to the radar site, data is not available due to the radar’s maximum tilt elevation of 60 degrees. The radar does not scan directly overhead. Live wind, rain, radar or temperature maps, more than 50 weather layers, detailed forecast for your place, data from the best weather forecast models with. This “anomalous propagation” phenomenon detects “sea return”, a phenomenon similar to ground clutter except that the echoes come from the sea surface. Under highly stable atmospheric conditions, like calm and clear nights or when there is a warm southerly wind blowing, the radar beam can be refracted almost directly into the sea at some distance from the radar, resulting in an area of intense looking echoes. To remove these unwanted reflections a filter is applied but it may also remove reflections from rain in the same area if these rain reflections are weaker than the ground clutter reflections. This results from the radio energy that is reflected back to the radar from these targets. It is only if the cloud stops completely over one area that all the 30mm fall into that area.Ĭoloumn Max: A display, in plan, of the maximum value of the reflectivity above each point at different altitudes of the area being observed, consequently, it is the maximum of PPIs (Plan Position Indicator) in the individual point.īuildings and hills in the vicinity of the radar produce what is known as “ground clutter” on the radar image which is highlighted by a dotted circle. One has to bear in mind that clouds move and this means that in one hour 30 mm of precipitation is spread over a very large area. The bright red means that rain is falling at the rate of 100 mm per hour, and the darkest blue means that the rain is falling at the rate of 0.1mm per hour. On the right hand side, underneath the date and time – which is in UTC (known also as GMT) and which is one hour behind Malta Winter Time, and two hours behind Malta Summer Time, one finds a table showing the rate of rainfall. This particular radar image shows the rate of rainfall in millimetres per hour of the ‘echoes’ produced. In short the display produced by the radar’s computer gives a horizontal map of where rain is falling and an estimate of how heavily it is falling. The “reflecting power” of the rainfall (which depends on the size of the raindrops and their concentration) is also calculated, thus providing an estimate of rainfall intensity unit used is the dBz. The radar’s computer determines the direction of the rain from the azimuth (orientation) of the antenna, and the distance to the rain from the time taken for the radar signal to return to the receiver.
Use the + or at the top right to zoom in. By finger pressure or mouse click you can move the area on the map.

With the cursor at the bottom left in the center you can view the weather over time. In RADAR (Radio Detection and Ranging), radio pulses are transmitted, in a highly focused beam, by a radar antenna and are reflected off objects and returned to a receiver at the antenna. The weather radar live itself displays cloud cover, current precipitation, storms, thunderstorms or tornados in real-time.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
